Introduction
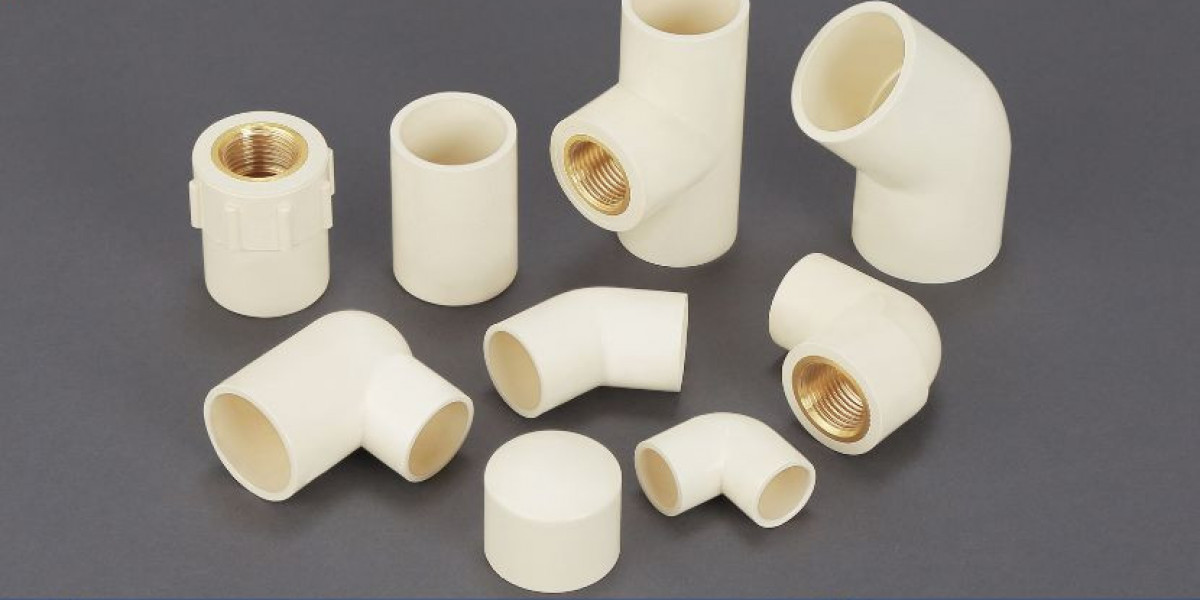
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) pipes are widely used in plumbing, industrial, and agricultural applications due to their excellent durability, resistance to high temperatures, and corrosion resistance. CPVC pipes are an essential component in various sectors, including construction, water supply, HVAC systems, and chemical industries. With increasing demand for safe, reliable, and long-lasting piping solutions, CPVC pipes have become a preferred choice for piping systems across the globe. Establishing a CPVC Pipe Manufacturing Plant can be a profitable business venture, especially in regions with rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and growing industrial activities. This CPVC Pipe Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines all the critical factors involved in setting up the plant, including market analysis, production processes, raw material requirements, financial considerations, and regulatory compliance.
What is CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride)?
CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) is a thermoplastic polymer made by chlorinating the polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The process of chlorination enhances the chemical and thermal resistance of the material, making it suitable for high-temperature applications, as well as offering enhanced durability compared to standard PVC pipes.
Key characteristics of CPVC pipes include:
High Temperature Resistance: CPVC pipes can handle temperatures up to 90°C (194°F), which is significantly higher than the maximum temperature tolerance of standard PVC pipes.
Corrosion Resistance: CPVC pipes are highly resistant to chemical corrosion, making them suitable for use in industries dealing with aggressive chemicals and substances.
Durability: CPVC pipes are durable, lightweight, and less prone to breaking or damage during installation and use.
Non-Toxic: CPVC is safe for potable water systems and complies with relevant health and safety standards.
Easy Installation: CPVC pipes are easy to install, with the ability to be joined using solvents and fittings, simplifying the installation process.
CPVC pipes are primarily used in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing systems, as well as in fire sprinkler systems, HVAC systems, and chemical processing applications.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Market Demand for CPVC Pipes
The demand for CPVC pipes is driven by a variety of factors, including:
Growing Infrastructure and Urbanization: With rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, especially in emerging economies, there is a substantial need for reliable and efficient piping systems. CPVC pipes are ideal for this purpose due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and pressure.
Plumbing and Water Distribution: The demand for CPVC pipes is high in residential and commercial plumbing systems due to their corrosion resistance, low cost, and easy installation. As the global population grows and new buildings and homes are constructed, the need for CPVC pipes continues to rise.
Chemical and Industrial Applications: CPVC pipes are used extensively in industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing due to their resistance to aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, and durability.
Replacement of Metal Pipes: In many regions, CPVC pipes are being used to replace traditional metal pipes (such as copper or iron pipes) due to their cost-effectiveness, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
Increased Focus on Sustainability: CPVC pipes are a sustainable choice for construction and infrastructure projects. Their long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements contribute to their increasing adoption.
Government Regulations and Safety Standards: CPVC pipes are ideal for water supply systems due to their non-toxic nature and ability to comply with health and safety regulations.
As a result, the global CPVC pipe market is expected to grow steadily in the coming years, driven by expanding construction activities and industrial needs.
Raw Materials for CPVC Pipe Production
The production of CPVC pipes requires specific raw materials that provide the necessary chemical, thermal, and physical properties. These include:
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): The base material for CPVC production is PVC resin, which is modified through chlorination to enhance its properties.
Chlorine Gas: Chlorine gas is used to chlorinate the PVC resin, enhancing its chemical and thermal resistance properties.
Impact Modifiers: These materials are added to improve the toughness and impact resistance of CPVC pipes, making them more durable.
Stabilizers: Stabilizers are used to prevent the degradation of CPVC during the manufacturing process. These stabilizers help maintain the material’s integrity and appearance.
Plasticizers: In some cases, plasticizers may be used to improve the flexibility and processing of the CPVC compound.
Pigments and Fillers: Pigments are used for coloring the pipes, while fillers help improve the pipe's overall performance and cost-effectiveness.
Solvents and Adhesives: Solvents are used to join CPVC pipes, and adhesives may be used for sealing joints during installation.
It is crucial to source high-quality raw materials from reliable suppliers to ensure the production of high-quality CPVC pipes.
CPVC Pipe Manufacturing Process
The CPVC pipe manufacturing process involves several steps to convert raw materials into finished pipes that meet the required specifications. The key stages in the process are:
1. Compounding
The first step in the CPVC pipe manufacturing process is the compounding of PVC resin with chlorine gas. The chlorine gas is introduced to the PVC resin in a controlled environment to create CPVC material. Additives such as stabilizers, impact modifiers, and fillers are also mixed in this stage to enhance the performance of the material.
2. Extrusion
Once the CPVC compound is prepared, it is fed into an extruder. The extrusion process involves melting the CPVC material and forcing it through a die to form the pipe shape. The pipe is then cooled as it exits the extruder, solidifying into its final form.
3. Sizing and Cooling
After extrusion, the pipe is passed through a sizing ring to ensure it maintains the desired diameter and thickness. The pipe is then cooled using a water bath or air cooling system to solidify the material and retain its shape.
4. Cutting and Lengths
Once the pipe has cooled and solidified, it is cut into the required lengths. These lengths are typically standardized according to the customer’s needs or industry specifications.
5. Quality Control
Quality control is a critical stage in the manufacturing process. Each batch of CPVC pipes is tested for quality assurance, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications for pressure, temperature resistance, and durability. Tests may include burst pressure tests, dimensional checks, and material composition analysis.
6. Printing and Packaging
The finished pipes are then printed with necessary labels, such as the manufacturer’s logo, size specifications, and safety warnings. The pipes are then packaged into bundles or cartons for transportation and distribution.
Investment and Financial Considerations
Setting up a CPVC pipe manufacturing plant involves substantial investment in machinery, raw materials, labor, and operational costs. The primary areas of expenditure include:
Land and Building: The plant requires a suitable location for manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution. Land acquisition and construction costs will vary depending on the region.
Machinery and Equipment: The machinery needed for extrusion, cooling, and cutting pipes includes extruders, molds, sizing rings, cooling tanks, and testing equipment. Investment in high-quality machinery is essential for efficient and reliable production.
Raw Materials: Initial procurement of PVC resin, chlorine gas, stabilizers, plasticizers, and other chemicals is necessary to kickstart production.
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the operation of machinery, quality control, maintenance, and management. Worker training on safety and proper handling of chemicals is essential.
Packaging and Distribution: The packaging of finished pipes and the establishment of distribution channels (local and international) will also require a portion of the initial investment.
Regulatory Compliance: There may be costs associated with obtaining certifications, ensuring compliance with local environmental and safety regulations, and meeting quality standards.
The payback period for a CPVC pipe manufacturing plant depends on the production scale, market demand, and operational efficiency. Typically, ROI can be achieved within 2-3 years if the plant is set up and managed efficiently.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Given the nature of the materials and processes involved in CPVC pipe production, manufacturers must comply with stringent regulatory and safety standards:
Quality Standards: CPVC pipes must meet international quality standards, such as ASTM D2846 and ISO 9001, ensuring the product is safe for use in plumbing and other applications.
Environmental Compliance: Manufacturers must comply with environmental regulations regarding waste disposal, emissions, and water usage. The production process must be designed to minimize environmental impact.
Workplace Safety: Safety standards must be implemented to protect workers from the chemicals used in the production process. Training programs and safety measures should be in place to prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment.
Health and Safety Standards: CPVC pipes are commonly used for potable water systems, so compliance with health and safety standards is crucial. Manufacturers must ensure that the pipes are non-toxic and safe for drinking water applications.
FAQs
1. What are CPVC pipes used for?
CPVC pipes are primarily used in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing systems, as well as in fire sprinkler systems, HVAC systems, and chemical processing.
2. What raw materials are required for CPVC pipe production?
Key raw materials include PVC resin, chlorine gas, stabilizers, impact modifiers, plasticizers, and fillers.
3. How are CPVC pipes manufactured?
CPVC pipes are manufactured through a compounding process, followed by extrusion, sizing, cooling, cutting, and quality control. The pipes are then packaged for distribution.
4. What are the advantages of CPVC pipes over other types of pipes?
CPVC pipes offer high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of installation. They are ideal for high-temperature water systems and chemical applications.
5. What certifications do CPVC pipes need?
CPVC pipes must meet quality standards such as ASTM D2846 and ISO 9001. Additionally, manufacturers must ensure compliance with health and safety regulations for potable water systems.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au