Compression therapy is a widely used treatment that applies controlled pressure to the limbs, improving blood circulation and reducing swelling. It is particularly effective for managing conditions such as venous insufficiency, lymphedema, and varicose veins, where poor blood flow leads to discomfort and tissue damage. Compression garments, bandages, and devices exert gentle pressure on the veins, encouraging blood to flow back toward the heart. By alleviating swelling and improving oxygen delivery to the tissues, compression therapy promotes faster healing and prevents complications like blood clots. It is a vital component of treatment for patients recovering from surgeries, injuries, or chronic conditions affecting circulation.
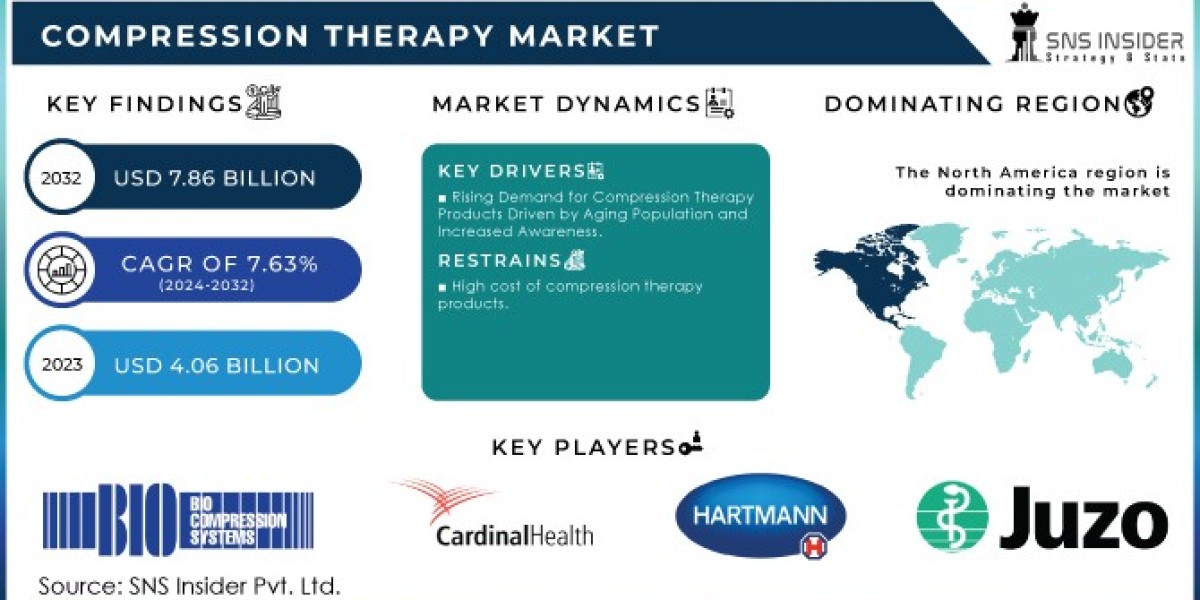
The Compression Therapy Market size was valued at USD 4.06 Billion in 2023 & is estimated to reach USD 7.86 Billion by 2032 with a growing CAGR of 7.63% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
Future Scope
The future of compression therapy is moving toward more personalized and technologically advanced solutions. Wearable compression devices equipped with sensors and digital monitoring are being developed to provide real-time feedback on the effectiveness of treatment. These devices will allow for continuous adjustments based on individual patient needs, ensuring optimal pressure is applied. Advances in materials science are also expected to improve the comfort and efficacy of compression garments, with innovations in breathable and moisture-wicking fabrics. As telemedicine grows, remote monitoring of patients using compression therapy could become more common, allowing healthcare providers to track progress and adjust treatments without in-person visits.
Trends
One of the key trends in compression therapy is the increasing use of advanced compression devices that provide intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) to stimulate circulation more effectively. Another trend is the development of smart compression garments, which integrate technology to monitor and adjust pressure levels automatically. These advancements are making compression therapy more accessible and efficient for patients with mobility issues or chronic conditions. Furthermore, compression therapy is increasingly being recommended as part of post-operative recovery protocols, particularly in orthopedic and cardiovascular surgeries, to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and improve recovery outcomes.
Applications
Compression therapy is used in various medical fields, particularly in treating conditions that cause poor circulation. It is commonly prescribed for patients with venous insufficiency, varicose veins, lymphedema, and DVT. It is also used as a preventive measure for individuals at high risk of blood clots, including those recovering from surgery or long periods of immobility. Athletes and individuals with active lifestyles also benefit from compression therapy to reduce muscle soreness and prevent injury. The therapy is integral to wound care management, helping heal ulcers, reduce swelling, and promote tissue repair.
Key Points
· Compression therapy improves circulation and reduces swelling in conditions like venous insufficiency and lymphedema.
· Future innovations include wearable compression devices with real-time monitoring and personalized pressure adjustments.
· Trends include the rise of smart compression garments and the use of compression therapy in post-operative care.
· Applications range from chronic condition management to post-surgery recovery and athletic injury prevention.
· Compression therapy plays a crucial role in enhancing healing and preventing complications like blood clots.
Conclusion
Compression therapy remains an essential treatment for managing circulation-related conditions and promoting healing. With advancements in smart devices and materials, the future of this therapy looks promising, offering patients more effective, personalized, and comfortable solutions. As it becomes more integrated into post-surgical recovery and chronic disease management, compression therapy will continue to enhance patient outcomes across a variety of medical fields.