Creative Diagnostics, a leading manufacturer and supplier of antibodies, antigens and assay kits, is pleased to announce the availability of its high-affinity Anti Venom Antibodies to researchers studying snakebite envenomation. These antibodies hold immense potential for improved snakebite treatments.
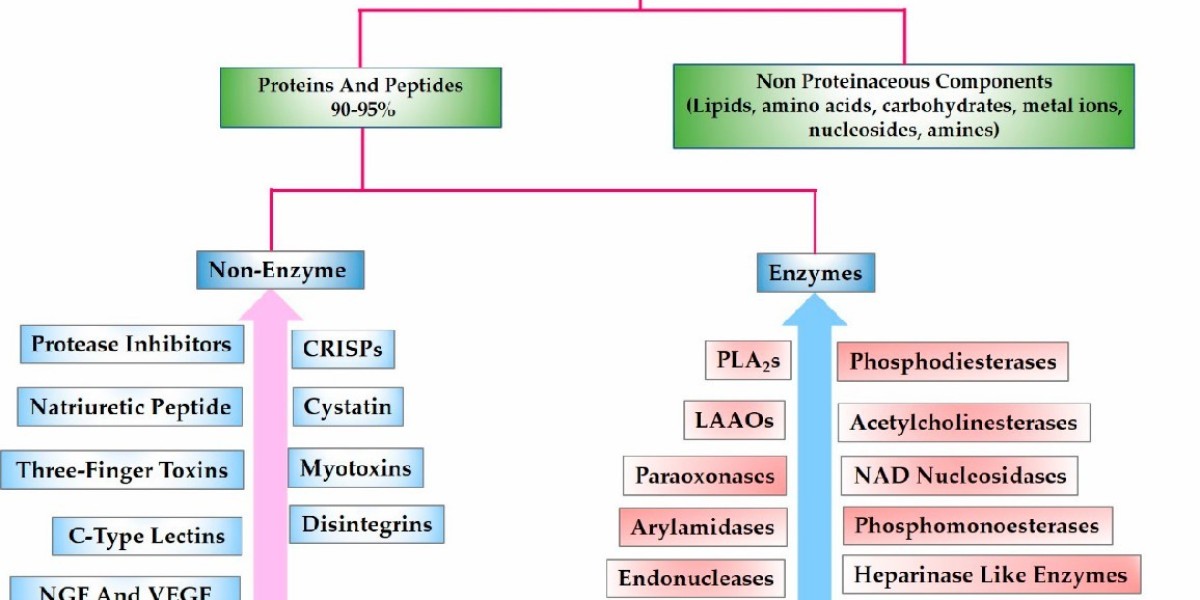
Snakebite envenomation is considered a neglected tropical disease that affects tens of thousands of people each year. Snake venom is an extremely complex mixture consisting mainly of proteins (±90-95%), in addition to peptides, carbohydrates, fragments of nucleic acid derivatives, metal ions, biogenic amines, lipids and free amino acids, which have different biological activities.
In general, viperid venoms are cytotoxic, hematotoxic, and occasionally myotoxic due to the fact that snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs) weaken capillaries and blood vessel walls, leading to hemorrhage. SVMPs and phospholipase A2 (PLA2) also cause tissue damage at the site of the bite, resulting in muscle weakness and tissue necrosis. On the other hand, elapid venoms (and a small percentage of viperid venoms) contains neurotoxins (which primarily cause systemic neurotoxicity) that block neuromuscular signaling. These toxins eventually block signaling to the lung muscles, causing respiratory paralysis and death.
Currently, the recommended treatment for snakebite is the use of antivenom or serum therapy, which treats snakebite by neutralizing the venomous toxins produced by snake venom. The most important clinical determinants in the treatment of snakebite are the type of antivenom to be used and the dose of antivenom. The specificity and dosage of antivenom depend on the accurate diagnosis of the snake. This requires the use of immunology-based assays, such as ELISA, to detect and quantify specific venoms to confirm the identity of the snake. In addition, the free venom of the patient is measured after therapy to determine if sufficient antivenom has been administered. Immunoassays can also be used to evaluate the cross-reactivity of antivenoms.
Effective antivenom therapy is critical to saving lives, but accurate diagnosis and appropriate antivenom selection are often challenging. Creative Diagnostics now offers a comprehensive portfolio of anti venom antibodies that target a broad range of toxins found in snake venom, providing researchers with valuable tools for the development of new and improved antivenom therapies. These new anti-venom polyclonal antibodies are specifically designed for research applications and are not intended for diagnostic use, such as the Sheep Anti-Vipera l atastei Venom PolyclonalAntibody (DPAB-JX2371341).
Creative Diagnostics is committed to advancing research in snakebite treatment. The release of these anti-venom antibodies demonstrates its commitment to advancing snakebite management to accelerate scientific research and development. Creative Diagnostics also offers custom antibody services and bulk production to support large-scale research efforts.
Creative Diagnostics’ Anti Venom Polyclonal Antibodies are meticulously designed to target specific snake venom toxins, making them ideal for research applications. For more information on the new antibodies, please visit https://www.creative-diagnostics.com/anti-venom-polyclonal-antibody.htm.
About Creative Diagnostics
Creative Diagnostics is a leading manufacturer and supplier of antibodies, viral antigens, innovative diagnostic components, and critical assay reagents. In addition to providing contract R&D and biologic manufacturing services for diagnostic manufacturers along with GMP biologics manufacturing for the biopharmaceutical market, the company aims to continue to act as a trusted source for all researchers’ assay development and manufacturing needs.