views
What is Multicasting in Computer Networks? A Beginner's Guide to Multicast Communication
In today's fast-changing computer network world, effective communication is the key. One such technique that makes data transmission efficient is multicasting. As an IT pro planning for certifications or a network enthusiast in search of enlightenment, knowing multicasting is important in computer networks. Through this UniNets guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of multicast communication, its uses, and how it varies from other types of transmissions.
Understanding Multicasting in Computer Networks
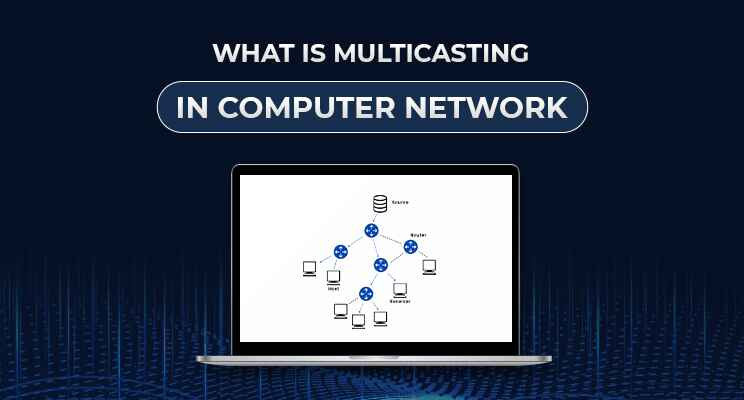
Multicasting is a form of communication where data is sent from one source to several selected recipients on a network. Multicast networks target only a specific set of devices that have subscribed to receive the data, whereas broadcasting (transmitting data to all devices) or unicasting (transmitting data to one device) does not.
Simply put, multicasting on computer networks makes efficient transmission of data such as live video streams, stock prices, or live online gaming data possible without taking up unnecessary bandwidth.
How Multicast Networks Work
In a multicast network, data is sent by the source device as one copy only, which is then replicated and distributed to several recipients who have subscribed to a given multicast group.
Routers on the network path handle the replication and transmission of data to the concerned receivers only.
Multicast communication depends on Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) in IPv4 or Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) in IPv6 to handle memberships in groups.
Key Features of Multicasting:
Effective bandwidth utilization
Supports scalable numbers of receivers
Low network congestion
Supports real-time applications such as IPTV, webinars, and VoIP
Use Cases of Multicasting in Networking
Multicasting is used in the large majority of computer networks today, particularly in enterprise and cloud-based setups. Many typical applications include:
Live video transmission
Online gaming and multiplayer applications
Real-time stock data updates
Software distribution in large-scale deployments
Webinars and online courses
At UniNets, cloud computing and network security students learn to comprehend and apply multicasting configurations on simulated as well as actual lab environments.
Comparison: Multicasting vs Broadcasting vs Unicasting
Type\tTarget\tEfficiency
Unicasting\tOne-to-One\tLow for many receivers
Broadcasting\tOne-to-All\tHigh traffic and unnecessary load
Multicasting\tOne-to-Many (Selective)\tHighly efficient
Whereas unicast is simple, it is inefficient with a large number of users. Broadcast, however, can overwhelm the network. This makes multicast in computer networks the perfect solution to send information to multiple interested recipients without overloading the infrastructure.
Multicasting and DHCP – A Connected Concept?
Whilst multicasting addresses group data transmission, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) guarantees that every device has the correct IP configuration to be part of such communications.
What is DHCP?
DHCP is an automatically configuring network protocol that provides IP addresses to devices in a network. It rescues administrators from the time-consuming process of manual setup.
The abbreviation of DHCP server is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server. It dynamically assigns IP address, default gateway, subnet mask, and DNS.
DHCP DORA Process Explained
The DHCP DORA process includes:
Discover: The client broadcasts to locate a DHCP server.
Offer: The server provides an IP address.
Request: The client requests the provided IP.
Acknowledge: The server acknowledges and assigns the IP.
At UniNets, students who are taking networking training and certification programs get practical experience in configuring DHCP servers and multicast traffic using routing protocols such as PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast).
Multicasting in Cloud Computing Times
The advent of cloud computing has further increased the significance of multicasting. Multicast protocols like AWS and Azure employed by cloud service providers distribute content between geographically dispersed servers and clients.
Examples of Cloud Computing Using Multicasting:
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Video conferencing software such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams
Real-time stock data portals
E-learning portals providing live classes
As a part of our cloud computing training at UniNets, students are given exposure to real-world cloud computing instances and are instructed on how multicast protocols collaborate with cloud environments for scalable data dissemination.
Certifications That Include Multicasting and Networking
To gain a solid foundation in computer networks and multicast communication, enroll in cloud certification training or network security courses. Some popular choices are:
CCNA and CCNP (Cisco) – basic and advanced networking
AWS Certified Advanced Networking – includes cloud-based multicast and routing
CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) – offers knowledge of network vulnerabilities, including multicast abuse
Multicasting in Ethical Hacking and Cybersecurity
Yes, even ethical hacking tutorials include topics on multicasting. Attackers can take advantage of multicast network vulnerabilities if not adequately protected. For instance, unauthorized joining of a multicast group can provide opportunities for packet sniffing or denial-of-service attacks.
During ethical hacking training online at UniNets, students are taught:
How to protect multicast communication
Identify unauthorized multicast group members
Track suspicious traffic for DHCP and IGMP
Ethical Hacking Salary and Career Scope
Studying multicasting, DHCP, and cloud infrastructure provides access to the field of cybersecurity. As per recent research, the salary of ethical hackers in India varies from ₹5 LPA for beginners to more than ₹20 LPA for experienced professionals with certified credentials such as CEH.
Enrolling in certified ethical hacking courses at UniNets teaches students not just technical skills, but also how network communication affects data privacy and infrastructure security.
Final Thoughts
Multicasting on computer networks is a dynamic communication that maximizes bandwidth, enhances performance, and facilitates scalable real-time data delivery. It underlies everything from live video streaming to cloud infrastructure and security.
Understand multicast networks, DHCP DORA process, and combining these with cloud computing certification and ethical hacking training to equip you for job demands in the IT sector. At UniNets, our certifications are crafted to bridge the gap between theory and hands-on implementation — so you're ready to take on the job in a competitive technology market.



Comments
0 comment