views
Historically, insurers granted broad system access to staff, which increased the risk of security breaches. That’s why more insurers are adopting a Zero Trust security model. This approach is built around a simple principle: trust nothing, verify everything.
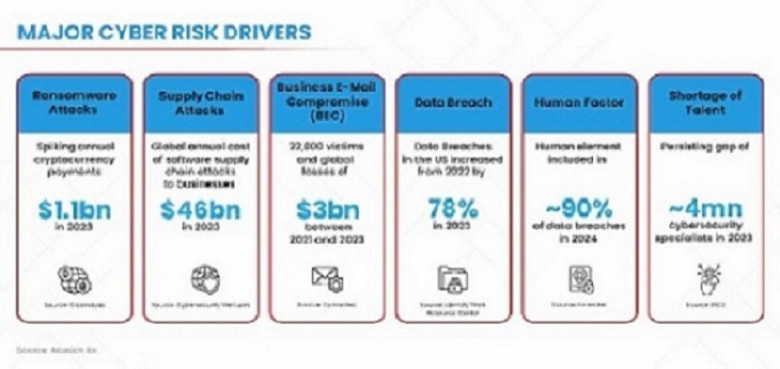
Here are some of the main elements that make up a Zero Trust architecture:
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Access isn’t granted until users confirm their identity through multiple methods—passwords, biometrics, or physical tokens. For roles like claims adjusters, a combination of all three might be required.
-
Microsegmentation: The platform is broken into smaller zones, so even if one section is compromised, the threat can’t spread easily across the network.
-
Behavioral Analytics: User activity is continuously tracked to identify unusual behavior, helping to detect insider threats or compromised accounts early.
For instance, Allianz reduced internal threat incidents by 40% using Microsoft Entra ID. By restricting each user’s access to only the data they need, they’ve significantly lowered their exposure to both accidental leaks and intentional misuse.
Cloud Security: Building Protection into Digital Infrastructure
As insurers continue moving their operations to the cloud, ensuring these environments are secure has become a top priority. This shift demands a new approach—cloud native security. Some of the strategies include:
-
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): These tools oversee cloud native security, flagging misconfigurations and suspicious access attempts.
-
AI-Powered DDoS Defense: Intelligent systems detect and respond to distributed denial-of-service attacks that could knock services offline.
-
Immutable Backups: Backups are locked and tamper-proof, so even in the case of a ransomware attack, data recovery is still possible.
Progressive Insurance, for example, has implemented Cloudflare-based protections to safeguard its digital claims portal from DDoS attacks, ensuring that customers always have access when they need it most.
Keeping Up with Compliance: Let Automation Do the Heavy Lifting
Regulatory compliance continues to be a major challenge for U.S.-based P&C insurers. From differing state privacy laws to evolving federal standards, the landscape is constantly changing—and failing to keep up can come with severe consequences.
The solution? Automated compliance systems built into core platforms. These intelligent engines use AI to cross-check policies against current regulations, identifying and flagging any discrepancies in real time. Think of it as having a built-in auditor reviewing every policy for you.
And the benefits go beyond avoiding penalties. These tools are also helping insurers save substantial resources. In fact, 78% of carriers now use automated compliance technology to manage the New York State Department of Financial Services’ 2024 AI underwriting rules—collectively sidestepping more than $2.3 million in potential fines.
Preparing for the Future: Quantum-Safe Encryption
Imagine a future where today’s encryption methods are rendered useless by quantum computers. While it might sound like science fiction, that future is fast approaching. Quantum computers could break through the cryptographic protections we currently rely on, putting sensitive data at risk.
To stay ahead, leading insurers are beginning to incorporate quantum-resistant algorithms into their platforms now. These encryption methods are designed to withstand quantum-level attacks, protecting customer and business data long into the future.
Munich Re, for example, is testing lattice-based cryptography to safeguard actuarial models and client data from quantum threats like Shor’s algorithm, which has the potential to crack RSA and ECC encryption.
The Bottom Line: Cybersecurity Needs to Be Baked Into the Core
In today’s digital environment, reactive cloud native security measures aren’t enough. P&C insurers must embed robust security protocols directly into the platforms that power their operations. The goal is simple: turn your core system into a digital fortress.
Looking for a core platform built with security at its heart? Explore what the SimpleINSPIRE system from SimpleSolve has to offer.



Comments
0 comment